Pot Odds Chart For Texas Holdem
Wizard Recommends
- Texas Holdem Odds And Probabilities
- Pot Odds Chart For Texas Holdem Table
- Pot Odds In Texas Holdem
- Pot Odds Chart For Texas Holdem Game
- Free Texas Holdem Against Computer
- Pot Odds Chart For Texas Holdem And Win
- $88 Free
- Free $20
- 100% up to $600
On This Page
Introduction
Rules
- A single 52-card deck is used. All cards count as its poker value. Aces may be high or low.
- One player is designated as the dealer, usually with a laminated marker. This person does not have to physically deal the game. However it is important that a symbolic dealer position rotate around the table.
- The player to the dealer's left must make a 'small blind' bet. The player to the left of the small blind must make a 'big blind' bet. The amounts of both blinds should be specified in advance. The purpose of the blinds is to get the ball rolling with some money in the pot.
- Two cards shall be dealt down to each player, starting with the person to the dealer's left.
- The player to the left of the big blind must either call or raise the big blind bet. The play in turn will go around the table according to normal poker rules, which I assume the reader already knows. Table rules will specify any limits on the size or number of allowed raises.
- The small blind may also raise the big blind. If nobody raises the big blind the player making the big blind has the option to raise his own bet. The term for this is the 'big blind option.'
- Three community cards will be dealt face up in the center of the table. This is called the 'flop.'
- Another round of betting will ensue, starting with the player to the dealer's left.
- A fourth community card will be dealt face up in the center of the table. This card is called the 'turn.'
- Another round of betting will ensue, starting with the player to the dealer's left. Generally the minimum bet is double the first two rounds of betting.
- A fifth and final community card will be dealt face up in the center of the table. This card is called the 'river.'
- Another round of betting will ensue, starting with the player to the dealer's left. The minimum bet is generally the same as the previous round.
Each player still in the game at the end will determine the highest poker value among his own two cards and the five community cards. It is NOT a requirement that the player use both of his own cards. The player with the hand of highest poker value shall win. Following are the hand rankings.
- Straight flush: Five consecutive and suited cards. For example 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
- Four of a kind: Four cards of the same rank, plus any fifth card. For example Q, Q, Q, Q ,4.
- Full house: Three of a kind and a pair. For example 6, 6, 6, J , J.
- Flush: Any five cards of the same suit, except for a higher ranking straight flush. For example A, Q, 8, 4 , 3.
- Straight: Five consecutive cards, except for a higher ranking straight flush. For example 8, 9, 10, J, Q.
- Three of a kind: Three cards of the same rank, plus any other two cards. For example 5, 5, 5, Q ,2 .
- Two pair: Two pairs, plus any fifth card. For example 8, 8, 2, 2 ,Q .
- Pair: A pair and any other three cards. For example 7, 7, 2, 5 ,A .
- ? High: Any five cards that do not form any higher poker hand. A king high hand for example might be K, Q, 7, 5 ,4 .
- If two or more players have poker values of the same rank then the individual cards will be used to break the tie. If necessary all five cards will be considered.
- I get asked a lot whether the two unused cards in a player's hand are used to break a tie. The answer is a firm NO. The two unused cards do not matter.
- If a new player arrives at the table he should either wait for the big blind position or put up an amount equal to the big blind, amounting to a call of the big blind.
- If a bet is made after another player runs out of money, then a separate pot is created. The player that ran out of money is not eligible to win the second pot. If more than one player runs out of money then multiple separate pots can be created.
- In formal games players may not bet with cash or buy chips with cash in the middle of a hand.
- There are numerous rules of etiquette, which I won't get into.
- There house may set the betting rules. There are three main types. A 'structured' game features raises of specified amounts. For example a '3/6 game' would mean that raises after the deal and flop are $3, and after the turn and river are $6. There is usually a limit to the number of raises a player may make, typically three. A 'pot limit' game has structured minimum raises but the maximum raise may be anything up to the amount in the pot at the time the raise is made. A 'no limit' game also has structured minimum raises but there is no maximum raise.
Nov 05, 2019 Below you will see our pot odds and outs chart, which shows the percentage of winning a hand by the turn/river or river only, depending on how many outs you have. You can right click and save the chart to your computer. If you don’t like memorizing charts then there are some shortcuts that can be. Dec 29, 2008 How to Calculate Pot Odds and Equity in Texas Holdem Understanding how to calculate pot odds is an absolutely fundamental skill to playing good poker. Understanding and calculating the pot odds, though, will only get you halfway to where you need to be.
Texas Holdem Odds and Pot Odds. Winning Texas holdem poker players have to have a solid understanding of odds and pot odds. Many inexperienced players make the mistake of assuming odds and pot odds are the same thing. While the two things are related, they aren’t the same. May 22, 2009 Pot odds are the odds you're 'being offered by the pot' to make your call. This is the amount of money in the pot compared to the amount of money you must pay to stay in the hand. An example: Say we go to the flop heads-up. There's $10 in the pot and your opponent bets $5. In poker there are good bets and bad bets – the game is simply a way of determining who can tell the difference. This is where the concept of pot odds comes into play. Put simply, pot odds means is there enough in the pot to call a bet. The fundamental principle of playing a drawing hand in poker is that you need a pot big enough to call. The world's most trusted Texas hold'em poker odds calculator. Improve your poker or find out just how bad that bad beat was. Use this handy list of what the odds are of improving your hand after the flop in Texas Hold'em, based on outs. Plus, how to use the rule of 4 and 2. Texas Hold'em Poker Odds Cheat Sheet Know Your Poker Hand Odds Based on Your Outs. Share PINTEREST Email. How to Split a Texas Hold'em Pot. 10 Ways to Beat the Odds at No-Limit Hold'em Poker.
Examples
Example 1
Board: A, 2, 4, 5, 6
Player 1: J, 6
Player 2: 7, Q
Player 1 wins. Slot price for lumia 920. Both have an ace high flush, so the second highest card is considered. Player 1's jack beats player 2's 7. The only way to have a flush tie is if the flush is entirely on the board and no hole cards are higher than the lowest card on the board in the same suit.
Example 2
Board: J, A, 7, 5, 6
Player 1: 2, J
Player 2: 10, J
Player 2 wins. Both have a pair of jacks so the singletons are considered. High highet singleton in both hands is an ace so the second highest singleton is considered. Player 1's second highest singleton is a 7, compared to player 2's 10. A 10 beats a 7 so player 2 wins.
Example 3
Board: A, A, K, Q, J
Player 1: Q, J
Player 2: Q, 2
Tie. Both have a two pair of aces and queens, with a king singleton. Some people incorrectly believe that in such cases the unused cards are considered, in this case player 1's pair of jacks beating player 2's jack/2. Only the top five cards matter. The jacks and deuce are irrelevant.
One of the most important aspects of Texas Hold'em is the value of each two-card hand before the flop. The decision of how to play your first two cards is something you face every hand, and the value of your first two cards is highly correlated to your probability of winning.
The following table shows my power rating for each initial 2-card hand in a 10-player game. The numbers are on a 0 to 40 scale. Basically, you should only play hands that are dark green, blue, or purple. Of course you should be more be more liberal in late position and picky in early position. If forced I would say you should need 10 points in late position and 19 points in early position to call the big blind. If your table is loose, as if often the case online, you can play a bit looser yourself.
Use the top table if you have a pair, the middle table if your cards are suited, and the bottom table if your cards are unsuited. Except for a pair,look up your high card along the left and your low card along the top.
Following are the links to my tables of the value of each intial hand according to the number of players. The 10-player section explains the methodology for creating the table table.
Pot Odds
The following table shows the probability of making various hands after the flop and the correct 'pot odds.' The pot odds are the breakeven ratio of money in the pot to the amount you have to bet for the player to be indifferent about calling, assuming the player would definitely win if he makes the hand (a big if) and there are no additional bets (another big if). This table is a good starting point the player should make mental adjustments for the probability of winning without making the hand, losing with making the hand, and expected future bets. The odds of a two pair improving to a full house are the same as those for four to an inside straight.
Pot Odds — After Flop
| Hand | Probability of Making Hand | Pot Odds |
|---|---|---|
| Four to a flush | 34.97% | 1.86 |
| Four to an outside straight | 31.45% | 2.18 |
| Four to an inside straight | 16.47% | 5.07 |
The next table shows the pot odds after the turn.
Pot Odds — After Turn
| Hand | Probability of Making Hand | Pot Odds |
|---|---|---|
| 4 to a flush | 19.57% | 4.11 |
| 4 to an outside straight | 17.39% | 4.75 |
| 4 to an inside straight | 8.70% | 10.50 |
Hand Strength Calculator
I'm proud to present my new and improved Poker Odds Calculator. Enter any situation in Texas Hold 'Em, and it will tell you the probability of each possible outcome.
Poker Tournament Calculator
My Poker Tournament Calculator will determine each player's probability, for up to nine players, of finishing in each place, and his expected share of any prize pool, assuming equal skill among all players. It produces the same results as what is known as the Independent Chip Model.
Internal Links
- Pinapple — Strategy and analysis of which card to discard before the flop.
- Bad Beat Jackpots: What is the Probability of Hitting one?
- Texas Hold 'Em Dominated Hand Probabilities: What is the probability one of your opponents has similar, and better, hole cards than yours?
In our poker math and probability lesson it was stated that when it comes to poker; “the math is essential“. Although you don’t need to be a math genius to play poker, a solid understanding of probability will serve you well and knowing the odds is what it’s all about in poker. It has also been said that in poker, there are good bets and bad bets. The game just determines who can tell the difference. That statement relates to the importance of knowing and understanding the math of the game.
In this lesson, we’re going to focus on drawing odds in poker and how to calculate your chances of hitting a winning hand. We’ll start with some basic math before showing you how to correctly calculate your odds. Don’t worry about any complex math – we will show you how to crunch the numbers, but we’ll also provide some simple and easy shortcuts that you can commit to memory.
Basic Math – Odds and Percentages
Odds can be expressed both “for” and “against”. Let’s use a poker example to illustrate. The odds against hitting a flush when you hold four suited cards with one card to come is expressed as approximately 4-to-1. This is a ratio, not a fraction. It doesn’t mean “a quarter”. To figure the odds for this event simply add 4 and 1 together, which makes 5. So in this example you would expect to hit your flush 1 out of every 5 times. In percentage terms this would be expressed as 20% (100 / 5).
Here are some examples:
- 2-to-1 against = 1 out of every 3 times = 33.3%
- 3-to-1 against = 1 out of every 4 times = 25%
- 4-to-1 against = 1 out of every 5 times= 20%
- 5-to-1 against = 1 out of every 6 times = 16.6%
Converting odds into a percentage:
- 3-to-1 odds: 3 + 1 = 4. Then 100 / 4 = 25%
- 4-to-1 odds: 4 + 1 = 5. Then 100 / 5 = 20%
Converting a percentage into odds:
- 25%: 100 / 25 = 4. Then 4 – 1 = 3, giving 3-to-1 odds.
- 20%: 100 / 20 = 5. Then 5 – 1 = 4, giving 4-to-1 odds.
Another method of converting percentage into odds is to divide the percentage chance when you don’t hit by the percentage when you do hit. For example, with a 20% chance of hitting (such as in a flush draw) we would do the following; 80% / 20% = 4, thus 4-to-1. Here are some other examples:
- 25% chance = 75 / 25 = 3 (thus, 3-to-1 odds).
- 30% chance = 70 / 30 = 2.33 (thus, 2.33-to-1 odds).
Some people are more comfortable working with percentages rather than odds, and vice versa. What’s most important is that you fully understand how odds work, because now we’re going to apply this knowledge of odds to the game of poker.
DO YOU PLAY TOURNAMENTS?
One of the most vital skills you can have is knowing when, and when not, to 3bet all-in preflop. Preflop aggression is crucial in middle-late stages, and this Crash Course will prepare you to 3bet like a pro from EVERY position. Stop guessing, start crushing, and 3bet your way to the final table.
Counting Your Outs
Before you can begin to calculate your poker odds you need to know your “outs”. An out is a card which will make your hand. For example, if you are on a flush draw with four hearts in your hand, then there will be nine hearts (outs) remaining in the deck to give you a flush. Remember there are thirteen cards in a suit, so this is easily worked out; 13 – 4 = 9.
Another example would be if you hold a hand like and hit two pair on the flop of . You might already have the best hand, but there’s room for improvement and you have four ways of making a full house. Any of the following cards will help improve your hand to a full house; .
The following table provides a short list of some common outs for post-flop play. I recommend you commit these outs to memory:
Texas Holdem Odds And Probabilities
Table #1 – Outs to Improve Your Hand
The next table provides a list of even more types of draws and give examples, including the specific outs needed to make your hand. Take a moment to study these examples:
Table #2 – Examples of Drawing Hands (click to enlarge)
Counting outs is a fairly straightforward process. You simply count the number of unknown cards that will improve your hand, right? Wait… there are one or two things you need to consider:
Don’t Count Outs Twice
There are 15 outs when you have both a straight and flush draw. You might be wondering why it’s 15 outs and not 17 outs, since there are 8 outs to make a straight and 9 outs for a flush (and 8 + 9 = 17). The reason is simple… in our example from table #2 the and the will make a flush and also complete a straight. These outs cannot be counted twice, so our total outs for this type of draw is 15 and not 17.
Anti-Outs and Blockers
There are outs that will improve your hand but won’t help you win. For example, suppose you hold on a flop of . You’re drawing to a straight and any two or any seven will help you make it. However, the flop also contains two hearts, so if you hit the or the you will have a straight, but could be losing to a flush. So from 8 possible outs you really only have 6 good outs.
It’s generally better to err on the side of caution when assessing your possible outs. Don’t fall into the trap of assuming that all your outs will help you. Some won’t, and they should be discounted from the equation. There are good outs, no-so good outs, and anti-outs. Keep this in mind.
Calculating Your Poker Odds
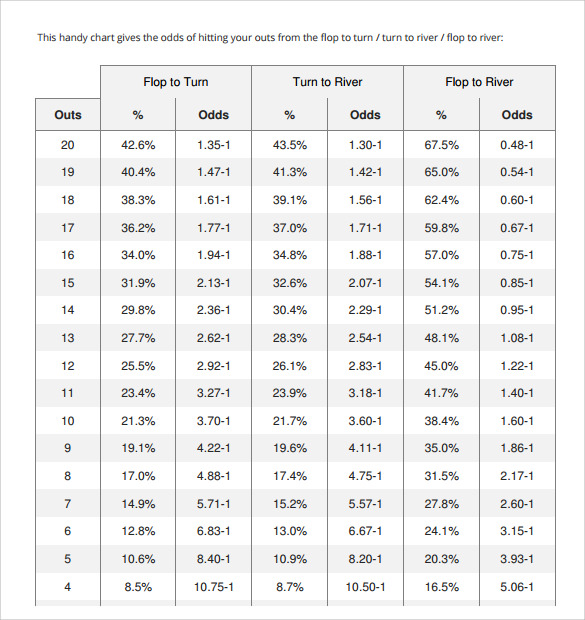
Once you know how many outs you’ve got (remember to only include “good outs”), it’s time to calculate your odds. There are many ways to figure the actual odds of hitting these outs, and we’ll explain three methods. This first one does not require math, just use the handy chart below:
Table #3 – Poker Odds Chart
As you can see in the above table, if you’re holding a flush draw after the flop (9 outs) you have a 19.1% chance of hitting it on the turn or expressed in odds, you’re 4.22-to-1 against. The odds are slightly better from the turn to the river, and much better when you have both cards still to come. Indeed, with both the turn and river you have a 35% chance of making your flush, or 1.86-to-1.
We have created a printable version of the poker drawing odds chart which will load as a PDF document (in a new window). You’ll need to have Adobe Acrobat on your computer to be able to view the PDF, but this is installed on most computers by default. We recommend you print the chart and use it as a source of reference. It should come in very handy.
Doing the Math – Crunching Numbers
There are a couple of ways to do the math. One is complete and totally accurate and the other, a short cut which is close enough.
Let’s again use a flush draw as an example. The odds against hitting your flush from the flop to the river is 1.86-to-1. How do we get to this number? Let’s take a look…
With 9 hearts remaining there would be 36 combinations of getting 2 hearts and making your flush with 5 hearts. This is calculated as follows:
(9 x 8 / 2 x 1) = (72 / 2) ≈ 36.
This is the probability of 2 running hearts when you only need 1 but this has to be figured. Of the 47 unknown remaining cards, 38 of them can combine with any of the 9 remaining hearts:
9 x 38 ≈ 342.
Now we know there are 342 combinations of any non heart/heart combination. So we then add the two combinations that can make you your flush:
36 + 342 ≈ 380.
The total number of turn and river combos is 1081 which is calculated as follows:
(47 x 46 / 2 x 1) = (2162 / 2) ≈ 1081.
Now you take the 380 possible ways to make it and divide by the 1081 total possible outcomes:
380 / 1081 = 35.18518%
This number can be rounded to .352 or just .35 in decimal terms. You divide .35 into its reciprocal of .65:
0.65 / 0.35 = 1.8571428
And voila, this is how we reach 1.86. If that made you dizzy, here is the short hand method because you do not need to know it to 7 decimal points.
The Rule of Four and Two
A much easier way of calculating poker odds is the 4 and 2 method, which states you multiply your outs by 4 when you have both the turn and river to come – and with one card to go (i.e. turn to river) you would multiply your outs by 2 instead of 4.
Imagine a player goes all-in and by calling you’re guaranteed to see both the turn and river cards. If you have nine outs then it’s just a case of 9 x 4 = 36. It doesn’t match the exact odds given in the chart, but it’s accurate enough.
What about with just one card to come? Well, it’s even easier. Using our flush example, nine outs would equal 18% (9 x 2). For a straight draw, simply count the outs and multiply by two, so that’s 16% (8 x 2) – which is almost 17%. Again, it’s close enough and easy to do – you really don’t have to be a math genius.
Do you know how to maximize value when your draw DOES hit? Like…when to slowplay, when to continue betting, and if you do bet or raise – what the perfect size is? These are all things you’ll learn in CORE, and you can dive into this monster course today for just $5 down…
Conclusion
In this lesson we’ve covered a lot of ground. We haven’t mentioned the topic of pot odds yet – which is when we calculate whether or not it’s correct to call a bet based on the odds. This lesson was step one of the process, and in our pot odds lesson we’ll give some examples of how the knowledge of poker odds is applied to making crucial decisions at the poker table.
Pot Odds Chart For Texas Holdem Table
As for calculating your odds…. have faith in the tables, they are accurate and the math is correct. Memorize some of the common draws, such as knowing that a flush draw is 4-to-1 against or 20%. The reason this is easier is that it requires less work when calculating the pot odds, which we’ll get to in the next lesson.
Related Lessons
Pot Odds In Texas Holdem
By Tom 'TIME' Leonard
Pot Odds Chart For Texas Holdem Game
Tom has been writing about poker since 1994 and has played across the USA for over 40 years, playing every game in almost every card room in Atlantic City, California and Las Vegas.